RBSE class 10 SST Chapter 15 Characteristics and unique trends of Indian Economy Notes
Economic reforms
After independence, India adopted the model of mixed economy and the policy of planned development. During 1950-1990, so many laws were made for functioning and management of the economy that the development process nearly came to a halt. Apart from this the government had to spend a substantial part of its resources on defence and other sectors.
The expenses of the government remain higher than its income. No concrete effort was made to control such expenses. Lack of fiscal discipline was clearly witnessed in government policies.
The government of India implemented economic reforms in July 1991 under the new economic policy. India requested for financial assistance from two international organisations named the World Bank and International Monetary Fund. These organisations provided loans to India on certain conditions. India followed this condition and announced a new economic policy in 1991 and implemented economic reforms.
Economic reforms were implemented through the process of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalisation.
Fiscal Discipline
Trade Deficit
Mixed Economy
Balance of Payments
World Bank
Liberalisation
Liberalisation is the process or means of the elimination of the control of the state over economic activities. OR means removing all unnecessary controls and restrictions like permits, licenses, quotas etc. imposed by the government.
It provides greater autonomy to the business enterprises in decision-making and eliminates government interference.
Since the adoption of the New Economic Strategy in 1991, there has been a drastic change in the Indian economy. With the arrival of liberalisation, the government has regulated the private sector organisations to conduct business transactions with fewer restrictions.
The economic liberalisation reduced all these obstacles and waived few restrictions over the control of the economy to the private sector.
Objectives of Liberalization
To boost competition between domestic businesses
To promote foreign trade and regulate imports and exports
Improvement of technology and foreign capital
To develop a global market of a country
To reduce the debt burden of a country
To unlock the economic potential of the country by encouraging the private sector and multinational corporations to invest and expand.
To encourage the private sector to take an active part in the development process.
To reduce the role of the public sector in future industrial development.
To introduce more competition into the economy with the aim of increasing efficiency.
Privatization
It means a transfer of ownership, management, and control of public sector enterprises to the private sector.
Under Privatization, disinvestment is also done in the government sector. This also a method of Privatization. In actual form, disinvestment is the process of the liquefying of assets, but in general form, it refers to selling of State's share in public sector undertaking to private sector.
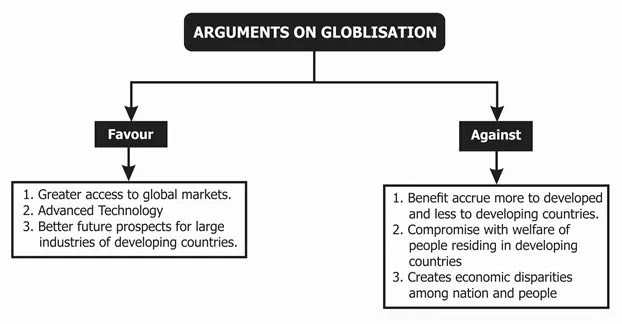
Globalization
The term Globalisation refers to the integration of the economy of the nation with the world economy.
multinational companies are playing an important role in the process of globalisation. A multinational company is one which controls and has ownership open production in more than one country. Development of information and communication technology has provided a rapid pace to globalisation, this has played a major role in spread of production and services in various countries. with the help of information and communication technology India also has obtained the benefit of globalisation by selling its service in the international market.
WTO (World Trade Organization) -
The World Trade Organisation was established on 1st January 1995. It performs the work of formation of trade policies and coordination between nations and also implements and controls multilateral trade agreements. It also settles trade disputes between various nations.
DG _ Ngozi Okonjo
The Concept of SWADESHI
The concept of swadeshi lays emphasis to use those goods and services which are made by Indian companies and industries within the country and the shun goods made by foreigner companies.
In the Swadeshi movement of Independence a policy of rehabilitation domestic industries and occupation and boycotting foreign goods was adopted.
Mahatma Gandhi used Swadeshi as a weapon in the freedom struggle.
Gandhiji made each and every Indian citizen aware of and inspired them to adopt Swadeshi
Mahatma Gandhi believed that India should also be self-dependent along with being independent and self-ruled.
the concept of Swadeshi lost its importance for sometime during the age of globalisation which started in the beginning of 1990.
Benefit of being Swadeshi____
Demand of goods produced by Indian industries will increase due to the concept of Swadeshi.Immense opportunities of development of Indian industries.
domestic product and national income of the country will rise due to adopting Swadeshi goods.
Indian companies are more laborious as compared to foreign companies. therefore along with the promotion of Swadeshi employment opportunities in India will also be increased definitely.
Due to increase in domestic production, imports will decline.
Foreign companies take away a large amount of wealth from India to their respective countries in the form of profit and dividends.
India's self dependence is increased by adopting Swadeshi. In situations of emergency, self dependence acts as a major protective layer.
The government receives comparatively greater revenue by increasing domestic production








0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box